零、输入输出
1、输入
主要使用 Console.Read() 和 Console.ReadLine() 方法。
2、输出
主要使用 Console.Write() 和 Console.WriteLine() 方法。
关于字符串格式化,参见:https://www.cnblogs.com/fskong/p/16940917.html
一、类与命名空间
1、概念
类(class)构成程序的主体
名称空间(namespace)以树型结构组织类(和其他类型)
能在命名空间中定义的元素有:类(Class),接口(Interface),结构(struct),委托(delegate),枚举(enum)
2、类库和引用
类库引用是使用名称空间的物理基础。不同技术类型的项目会默认引用不同的类库。
- DLL 引用(黑盒引用,无源代码)
- 项目引用(白盒引用,有源代码)
3、类的三大成员
- 属性
- 方法
- 事件
- 类或对象通知其它类或对象的机制,为C#所特有
- 善用事件机制非常重要
各种类的侧重:
- 模型类或对象重在属性,如 Entity Framework
- 工具类或对象重在方法,如 Math,Console
- 通知类或对象重在事件,如各种 Timer
4、静态成员与实例成员
- 静态(Static)成员在语义上表示它是“类的成员”
- 实例(非静态)成员在语义表示它是“对象的成员”
- 绑定(Binding)指的是编译器如果把一个成员与类或对象关联起来
二、数据类型
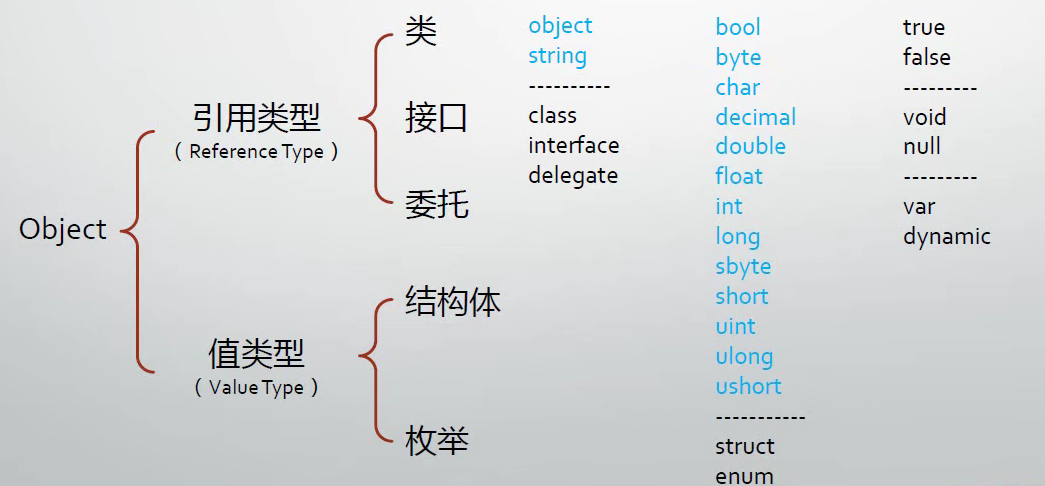
1、五大类型
- 类(classes)如:Window, Form, Console, String
- 结构体(structures)如:Int32, Int64, Single, Double
- 枚举(Enumerations)如:HorizontalAlignment, Visibility
- 接口(Interfaces)
- 委托(Delegates)
类型的派生谱系:
2、基本数据类型
| 类型 | 描述 | 范围 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| bool | 布尔值 | true 或 false | False |
| byte | 8 位无符号整数 | 0 到 255 | 0 |
| char | 16 位 Unicode 字符 | U +0000 到 U +ffff | ‘\0’ |
| decimal | 128 位精确的十进制值,28-29 有效位数 | (-7.9 x 1028 到 7.9 x 1028) / 100 到 28 | 0.0M |
| double | 64 位双精度浮点型 | (+/-)5.0 x 10-324 到 (+/-)1.7 x 10308 | 0.0D |
| float | 32 位单精度浮点型 | -3.4 x 1038 到 + 3.4 x 1038 | 0.0F |
| int | 32 位有符号整数类型 | -2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647 | 0 |
| long | 64 位有符号整数类型 | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 到 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 | 0L |
| sbyte | 8 位有符号整数类型 | -128 到 127 | 0 |
| short | 16 位有符号整数类型 | -32,768 到 32,767 | 0 |
| uint | 32 位无符号整数类型 | 0 到 4,294,967,295 | 0 |
| ulong | 64 位无符号整数类型 | 0 到 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 | 0 |
| ushort | 16 位无符号整数类型 | 0 到 65,535 | 0 |
另外:
- 可以使用
var关键字在定义时使用类型推导。 - 可以使用
dynamic关键字定义“动态类型”的变量,将不会在编译期进行类型检查。
三、运算符
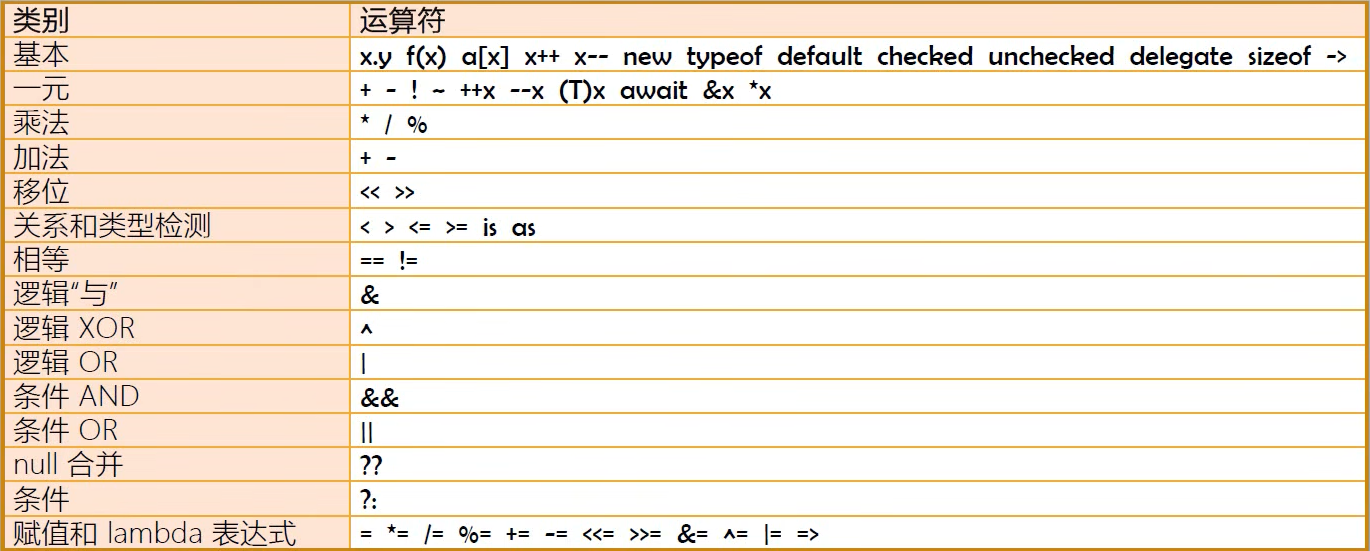
1、运算符种类与特点
运算符重载:
class Person {publicstaticoperator +(Person a, Person b) {// place your code }} default 运算符:https://blog.csdn.net/wsnbbdbbdbbdbb/article/details/125786005
checked, unchecked 是用来检查溢出异常的,可以以上下文形式使用:
checked {try { uint y = uint.MaxValue + 1; Console.WriteLine(y); }catch (OverflowException e) { Console.WriteLine("发生溢出"); }} delegate 是用于实现委托的运算符,也可以被用来实现匿名方法,不过目前更推荐使用 lambda 表达式。
new 运算符的一些用法:
staic void Main(string[] args) {// 使用初始化器 Form myForm = new Form() { Text="Hello World" }// 创建匿名类对象 var person = new { Name="Person88", Age=34 }}2、类型转换
- 隐式(implicit)类型转换
- 不丢失精度的转换
- 子类向父类的转换
- 装箱
- 显式(explicit)类型转换
- 有可能丢失精度(甚至发生错误)的转换,即 cast
- 拆箱
- 使用Convert类
- ToString 方法与各数据类型的 Parse/TryParse 方法
- 自定义类型转换操作符
// cast:int a = (int) double_value;// Convert 类方法:Convert.ToDouble(the_str);// ToString 方法:the_int.ToString();// Parse 和 TryParse:double.Parse(); // 失败直接抛出异常double.TryParse(); // 返回值为 bool 值,判断是否转换成功// 自定义显式转换 A var1 = (A) var2;public static explicit operator A(B var2) {// 转换方法,返回 A 类对象}// 自定义隐式转换 A var1 = var2;public static implicit operator A(B var2) {// 转换方法,返回 A 类对象}3、is 和 as
is 示例:
// 假设 Teacher 类继承于 HumanTeacher t = new Teacher();Console.WriteLine(t is Human); // true as 示例:
object o = new Teacher();if (o is Teacher) { Teacher t = (Teacher) o; t.Teach();}// 等价于:Teacher t = o as Teacher;if (t != null) { t.Teach();}4、可空类型
// 定义 x 为可空 intint? x = null;x = 100;Console.WriteLine(x);Console.WriteLine(x.HasValue);// 如果是 null,赋值为 1int y = x ?? 1;Console.WriteLine(y);// 当不为空时,和 2 比较是否相等x?.Equals(2);四、表达式和语句
1、标签语句和块语句
staic void Main(string[] args) {// 一个块语句是独立的上下文环境 { hello: Console.WriteLine("Hello~");goto hello; }}2、switch 语句
switch(score) {case score >= 80 && score <= 100:// ...break;case score >= 60 && score < 80:// ...break;// case 为 1 和 2 共用一个 sectioncase1:case2:// ...break;default:// throw errorbreak;}3、try-catch-finally 语句
try {// ...}catch (aException e) {// e 是异常对象 Console.WriteLine(e.Message);}catch (bException e) {// ...}finally {// ...} 抛出异常:
catch(xxx e) {throw;}// 或catch (xxx e) {throw e;}// 或catch (xxx e) {thrownew xxx("custom message");}// 或thrownew xxx; 详细区别见于:https://blog.csdn.net/zwb_578209160/article/details/119384988
4、循环迭代
while、do-while、for 语句与 C 基本类似。
关于 C# 的迭代器和迭代实质:
List<int> intList = new List<int>() {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};IEnumerator iterator = intList.GetEnumerator();while (iterator.MoveNext()) { Console.WriteLine(iterator.Current);} 而 foreach 方法则是内部实现了这个过程:
List<int> intList = new List<int>() {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};foreach(var elem in intList) { Console.WriteLine(elem);}五、方法参数传递
1、值参数
- 传递前,必须先明确赋值
- 对于值类型,参数创建变量的副本
- 对于引用类型,参数赋值前是引用,赋值后是新的对象
- 对于引用类型,直接修改参数,则外部对象随之改变(此时参数和外部值指向的地址是相同的,都指向于堆内存的同一块区域)
2、引用参数
static void hasSideEffect(ref int x, ref int y) { x = 1; y = 2;}- 传递前,必须先明确赋值
- 对于值类型,参数不创建变量的副本
- 对于引用类型,参数赋值前是引用,赋值后将会覆盖外部对象。
- 对于引用类型,直接修改参数,则外部对象随之改变。(此时参数和外部值指向的地址是不同的,参数先指向外部值,外部值指向堆内存中的一块区域)
- 一般用作“改变”操作
3、输出参数
class DoubleParser {public static bool TryParse(string input, out double? result) {try { result = double.Parse(input);returntrue; } catch { result = null;returnfalse; } }}// 使用double x;bool status = DoubleParser.TryParse("123.45", out x);if (!status)thrownew Exception("转换错误");Console.WriteLine(x);- 传递前,可以先不赋值,但是在方法内部必须有赋值。
- 对于值类型和引用类型的相关特点,和引用参数类似。
- 一般用作“输出”操作
4、数组参数
static int GetSum(params int[] intArr) {int sum = 0; foreach(var elem in intArr) { sum += elem; }return sum;}// 以下传值方法皆可:GetSum(1, 2, 3);GetSum(newint[] {1, 2, 3});- 只能有一个且必须是形参列表中的最后一个,由 params 修饰
5、具名使用
Student stu = new Student(name: "123", age: 18);
- 参数位置不再受约束
6、可选参数(默认参数)
和其他语言类似。
7、扩展方法
在不修改源码,或重新编译 dll 的情况下,进行方法扩展:
// 声明静态类staticclass DoubleExtension {public static double Round(this double input, int digits) {return Math.Round(input, digits); }}// 使用double x = 3.1415926535d;x.Round(4);- 方法必须是公有、静态的,即被
public static所修饰 - 必须是形参列表中的第一个,由
this修饰 - 必须由一个静态类(一般类名为 xxxExtension )来统一收纳对 xxx 类型的扩展方法
六、类、枚举和结构体
1、构造,析构和重载
重载:
class Student {publicint ID;publicstring Name;public Student() {this.ID = 1;this.Name = "Hello"; }public Student(int id, string name) {this.ID = id;this.Name = name; }} 基本原理和细节与 C++ 类似。
静态构造函数:
// 静态构造函数只能用于构造静态成员,且必然会先被调用class Student {static Student() { Console.WriteLine("静态构造方法必然先被调用"); }public Student(string str) { Console.WriteLine(str + "你好呀"); }} 析构:
class Student { ~Student() { Console.WriteLine("析构完成"); }} 析构无修饰符,无参,无继承和重载。
2、默认访问权限
默认访问权限:
- 命令空间中只能使用 public 和 internal 两种访问修饰符,默认为 internal。
- 枚举、接口默认访问权限为 public,不能修改且不能使用访问修饰符。
- 类默认为 internal 访问修饰符。 构造函数默认为 public 访问修饰符。
- 析构函数不能显式使用访问修饰符且默认为 private 访问修饰符。
- 类的成员默认访问修饰符为 private。
- 嵌套类型的默认访问修饰符为 private。
- 派生类的可访问性不能高于基类。成员的可访问性决不能高于包含类的可访问性。
3、方法重载
方法重载需要的条件:
- 方法名相同
- 具有不同的参数个数或参数类型或参数顺序,与参数名无关
注意:
- 传值参数同时可以与引用参数、输出参数中的一个重载。
- 方法重写和覆写与重载不同
4、partial
partial 可以将类、接口或接口的定义拆分到多个源文件中。方便扩展和管理。
// Book.csnamespace BookStore {public partial class Book {publicint ID {get; set;}publicstring Name {get; set;}publicdouble Price {get; set;}publicstring Author {get; set;} }}// BookExtends.csnamespace BookStore {public partial class Book {public void Show() { Console.WriteLine($"Book {Name}'s price is {Price}."); } }}5、类其他知识
类访问权限:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45037155/article/details/123658777
关于继承:https://blog.csdn.net/QWD8596/article/details/120819502
关于静态成员继承:https://blog.csdn.net/WuLex/article/details/119342955
关于密封(sealed):https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43024228/article/details/89885161
关于重载和多态:默认不需要 virtual 和 override 关键字,子类也可以实现重写。但是这些是实现多态的重要手段。此部分参考:http://t.zoukankan.com/dotgua-p-6287926.html
关于字段,属性和访问器:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44023930/article/details/123447507 (为区分,字段首字母小写,而属性首字母大写)
关于抽象类和抽象方法:
- 抽象方法只在抽象类中定义
- 继承的实现类通过 override 修饰实现虚方法
关于抽象属性:
- 只在抽象类中定义
- 至少一个访问器
- 详细参见:https://blog.csdn.net/chenweicode/article/details/98849554
6、枚举
枚举:
- 人为限定取值范围的整数
- 整数值的对应
- 比特位式用法
enum Level { Employee, Manager, Boss, BigBoss}// 使用static void Main() { Level lvl = Level.Boss;} 注:默认从 0 开始编号,以 1 递增
也可以自己赋值:
// 此时 BigBoss 为 301enum Level { Employee=100, Manager=200, Boss=300, BigBoss} 比特位用法:(用于标记和识别是否具有某些特质)
enum Skill { Drive = 1, Cook = 1<<1, Program = 1<<2, Teach = 1<<3}staticvoid Main() { Skill HasSkill = Skill.Drive | Skill.Cook | Skill.Program | Skill.Teach;// 判断是否会编程 Console.WriteLine((HasSkill & Skill.Program) != 0);}7、结构体
结构体:
- 值类型,可装箱、拆箱
- 可实现接口,但不能派生自类或结构体
- 不能有显式无参构造器,但可以有显式有参构造器
interface ISpeak {void Speak();}struct Student: ISpeak {publicint ID {get; set;}publicstring Name {get; set;}public void Speak() { Console.WriteLine($"I'm {ID} student {Name}."); }}static void Main() { Student stu = new Student() {ID=101, Name="MelodyEcho"};// 装箱和拆箱 object obj = stu; Student stu2 = (Student) obj;// 拷贝生成新的值,而不是产生引用 Student stu3 = stu;}七、字段、属性、索引器和常量
1、字段
简述:
- 字段(field)是一种表示与对象或类型(类与结构体)关联的变量。
- 尽管字段声明带有分号,但它不是语句
- 字段的名字一定是名词
字段的初始值:
- 无显式初始化时,字段获得其类型的默认值,所以字段永远都不会未被初始化
字段的修饰符:
- new
- public, protected, internal, private
- static
- readonly
- volatile
new 修饰符用于隐藏子类中继承的父类成员,以实现重写:
publicclass Base {publicclass Nested {};publicint var1;public void method() {}}class Sub: Base {newpublic class Nested {};newint var1;newvoid method() {}} volatile :多个线程同时访问一个变量,CLR 为了效率,允许每个线程进行本地缓存,这就导致了变量的不一致性。volatile 就是为了解决这个问题,volatile 修饰的变量,不允许线程进行本地缓存,每个线程的读写都是直接操作在共享内存上,这就保证了变量始终具有一致性。
public volatile int x;
readonly:只读成员。
- 与
get{}区别:- readonly 只能够初始化一次,即在定义或者构造方法初始化时。而
get{}虽然也起到的只读的作用,但可以通过set{}进行多次修改。
- readonly 只能够初始化一次,即在定义或者构造方法初始化时。而
- 与
const对比:- const 常量必须要有初始值,而 readonly 可以没有
- readonly 可以在构造方法中进行赋值,而 const 不行。const 一旦确定值就不可以改变了
2、属性
属性(property):是一种用于访问对象或类型的特征的成员,特征反映了状态。
- field 更偏向于实例对象在内存中的布局,property 更偏向于反映现实世界对象的特征
- 对外:暴露数据,数据可以是存储在字段里的,也可以是动态计算出来的
- 对内:保护字段不被非法值“污染”
- 属性大多数情况下是字段的包装器(wrapper)
建议:永远使用属性(而不是字段)来暴露数据。
class Person {// 完整声明privateint age;publicint Age { get{ returnthis.age; }set {if (value >= 0 && value <= 120) {this.age = value; }else {thrownew Exception("超出范围的值") } } }// 简略声明publicint Height { get; set; }}// 控制访问级别:publicint Height { set; privateset; }3、索引器
索引器(indexer):一种成员。它使对象能够用与数组相同的方式(即使用下标)进行索引。
索引器的声明:
class StuScore {private Dictionary<string, int> dict = new Dictionary<string, int>();publicint ? this[string subject] { get {if (this.dict.ContainsKey(subject))returnthis.dict[subject];elsereturn null; }set {if (!value.HasValue)thrownew Exception("不能为空值");if (this.dict.ContainsKey(subject))this.dict[subject] = value.Value;elsethis.dict.Add(subject, value.Value); } }} 使用:
StuScore score = new StuScore();Console.WriteLine(score["Math"]);score["Math"] = 123;Console.WriteLine(score["Math"]);score["Math"] = null;Console.WriteLine(score["Math"]);4、常量
常量(constant):是表示常量值的类成员。(即可以在编译时计算的值)
常量隶属于类型而不是对象,即没有“实例常量”。“实例常量”的角色由只读实例字段来担当。
同时注意:当希望成为常量的值其类型不能被常量声明接受时(类/自定义结构体),应该使用静态只读字段:
class Building {// MetaInfo 是自定义的类publicstatic readonly MetaInfo Meta = new MetaInfo();}八、泛型
泛型可以很好地解决类型膨胀和成员膨胀的问题。
1、泛型类
class Apple {publicstring Color {get; set;}}class Book {publicstring Name {get; set;}}class Box<TCargo> {public TCargo Cargo {get; set;}}static void Main() { var apple = new Apple() {Color="Red"}; var book = new Book() {Name="New Book"};// 特化 Box<Apple> box = new Box<Apple>() {Cargo=apple}; box<Book> box2 = new Box<Book>() {Cargo=book};}2、泛型接口
interface IUnique<T> { T ID {get; set;}}class Student<T>: IUnique<T> {public T ID {get; set;}publicstring Name {get; set;}}// 也可以直接在实现时特化class StudentSecond: IUnique<ulong> {public ulong ID {get; set;}publicstring Name {get; set;}}static void Main() { Student<int> stu = new Student<int>(); stu.ID = 123; var stu2 = new Student<string>(); stu2.ID = "100";}3、泛型方法
static T[] Zip<T>(T[] a, T[] b) { T[] zippped = new T[a.Length + b.Length];int ai = 0, bi = 0, zi = 0;do {if (ai < a.Length) zipped[zi++] = a[ai++];if (bi < b.Length) zipped[zi++] = b[bi++]; }while (ai < a.Length || bi < b.Length);return zipped;}九、委托
委托(delegate)是函数指针的“升级版”。
1、使用内置委托类型
// 无返回值、无参数委托// 此处传递的方法为无返回值、无参数方法Action action = new Action(Calculator.ReportMethodsNum);// 触发,以下两种写法皆可action.Invoke();action();// 无返回值、有参数委托Action<string> action = new Action(StringManager.input);action.Invoke("abc");action("edf");// 有返回值委托// 假设传递的方法参数类型为:int, int,返回值类型为:floatFunc<int, int, float> func = new Func<int, int, float>(Calculator.Div);// 触发,以下两种写法皆可float res = func.Invoke(2, 3);float res = func(2, 3);2、自定义委托
- 委托是一种类(class)。
- 类是数据类型所以委托也是一种数据类型
- 一般推荐声明在命令空间下,而不是嵌套在类中
- 委托与所封装方法必须类型兼容
- 返回值数据类型一致
- 参数列表在个数和数据类型上一致,参数名不需要一致
public delegate double Calc(double x, double y);class Program {class Calculator {public double Add(double x, double y) {return x + y; } }static void Main() { Calculator calculator = new Calculator(); Calc calc1 = new Calc(calculator.Add); Console.WriteLine(calc1.Invoke(1, 2)); Console.WriteLine(calc1(1, 2)); }} 主要作用:把方法当作参数传给另一个方法
- 模板方法,“调用”指定的外部方法来产生结果
- 回调(callback)方法,调用指定的外部方法
3、自定义泛型委托
public delegate T MyDele<T>(T a, T b);static void Main() { MyDele<int> deleAdd = new MyDele<int>(Add);int res = deleAdd(100, 200); MyDele<double> delMul = new MyDele<double>(Mul);double res2 = delMul(100.2, 300.5);}static int Add(int a, int b) {return a + b;}static double Mul(double a, double b) {return a * b;}4、多播委托与委托隐式异步
多播委托(同步调用):
Action act1 = new Action(stu1.DoHomework);Action act2 = new Action(stu2.DoHomework);act1 += act2;// 此后执行顺序按合并顺序act1.Invoke(); 委托隐式异步:
// 每一个 act 都在一个子线程中执行,默认不加锁act1.BeginInvoke(null, null);act2.BeginInvoke(null, null);5、Lambda 表达式与匿名函数
Func<int, int, int> func = (int a, int b) => { return a + b; };// 因为指定了委托的参数和返回值类型,所以可以不写类型Func<int, int, int> func = (a, b) => a+b; 组合使用:(泛型方法、泛型委托参数)
staticvoid DoSomeCalc<T>(Func<T, T, T> func, T x, T y) { T res = func(x, y); Console.WriteLine(res);}// 使用时:DoSomeCalc((a, b) => a+b, 1, 2);6、Linq
Linq:语言集成化查询(Language Integrated Query)
参考:https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/csharp/linq/write-linq-queries
十、事件
角色:使对象或类具备通知能力的成员
使用:用于对象或类间的动作协调与信息传递(消息推送)
五个组成部分:
- 事件的拥有者(event source,对象)
- 事件成员(event,成员)
- 事件的响应者(event subscriber,对象)
- 事件处理器(event handler,成员)—— 本质上是一个回调方法
- 事件订阅——把事件处理器与事件关联在一起,本质上是一种以委托类型为基础的“约定”
特点:是委托的封装。保证了委托不在外部被随意的触发和调用,而只是暴露添加和移除事件处理器的功能。
1、事件常见类型
事件拥有者和事件响应者在不同的类:
class Program {static void Main() { Form form = new Form(); Controller controller = new Controller(form); form.ShowDialog(); }}class Controller {private Form form;public Controller(Form form) {if (form != null) {this.form = form;this.form.Click += this.FormClicked; } }private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e) {this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString(); }} 事件拥有者和事件响应者是同一对象:
class Program {static void Main() { MyForm form = new MyForm(); form.Click += form.FormClicked; form.ShowDialog(); }}class MyForm: Form {internal void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e) {this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString(); }} 事件拥有者是事件响应者的成员:
class Program {static void Main() { MyForm form = new MyForm(); form.ShowDialog(); }}class MyForm: Form {private TextBox textbox;private Button button;public MyForm() {this.textBox = new TextBox();this.button = new Button();this.Controls.Add(this.textBox);this.Controls.Add(this.button);this.button.Click += this.ButtonClicked; }private void ButtonClicked(object sender, EventArgs e) {this.textBox.text = DateTime.Now.ToString(); }}2、事件完整声明
using System;class Program {static void Main() { Customer customer = new(); Waiter waiter = new(); customer.WhenOrder += waiter.AcceptOrder; customer.Order(); customer.Pay(); }}// 传递事件消息的类(定义事件发生时传递的参数)publicclass OrderEventArgs: EventArgs {publicstring DishName {get; set;}publicstring Size {get; set;}}// 事件提供者publicclass Customer {// 委托声明(定义事件处理器的规格)public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e);// 委托字段(用于保存所有的委托,即事件处理器)private OrderEventHandler oeHandler;// 事件成员public event OrderEventHandler WhenOrder { add {oeHandler += value;} remove {oeHandler -= value;} }publicdouble Bill {get; set;}public void Pay() { Console.WriteLine("The customer Pay ${0}.", this.Bill); }// 事件触发public void Order() {if (oeHandler != null) { OrderEventArgs e = new() { DishName = "Kongpao Chicken", Size = "large" }; oeHandler.Invoke(this, e); } }}// 事件响应者publicclass Waiter {public void AcceptOrder(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("The waiter had served the dish:\n{0}, size: {1}", e.DishName, e.Size);double price = 10;switch (e.Size) {case"small": price *= 0.5;break;case"large": price *= 1.5;break;default:break; } customer.Bill += price; }}3、事件简略声明
简略声明类似于字段式声明(field-like)
/* * 其他部分相同,只需要更改以下部分 */// 只定义事件字段// 此时不显式定义委托字段,因此委托字段使用同一名字访问// 这种写法是一个语法糖,但实际在编译后,内部是有着委托字段的public event OrderEventHandler WhenOrder;// 事件触发public void Order() {if (WhenOrder != null) { ... WhenOrder.Invoke(this, e); }}十一、接口与抽象类
1、简述
概念:
- 抽象类是未完全实现逻辑的类(可以有字段和非 public 成员,它们代表了“具体逻辑”)
- 为复用而生,也具有解耦功能
- 接口是完全未实现逻辑的“类”(即纯虚类,只有函数成员,成员全部 public)
- 为解耦而生,方便单元测试
共同点:都不能实例化,只能用来声明变量、引用具体类的实例
区别和联系:https://www.infoworld.com/article/2928719/when-to-use-an-abstract-class-vs-interface-in-csharp.html
使用范例:
interface IVehicle {void Stop();void Fill();void Run();}abstract class Vehicle: IVehicle {public void Stop() { Console.WriteLine("Stopped."); }public void Fill() { Console.WriteLine("Pay and fill."); }abstract public void Run();}class Car: Vehicle {public override void Run() { Console.WriteLine("Car is running."); }}2、接口显式实现
interface ISecret {void DoSomethingSecret();}interface IPublic {void DoSomethingExplicit();}class Person: ISecret, IPublic {public void DoSomethingExplicit() { Console.WriteLine("The thing that Everyone knows."); }void ISecret.DoSomethingSecret() { Console.WriteLine("The thing that only I know. "); }}static void Main() { var publicPerson = new Person(); publicPerson.DoSomethingExplicit();// 也可以使用强制类型转换 var privatePerson = publicPerson as ISecret; privatePerson.DoSomethingSecret();} DoSomethingSecret() 方法显式实现,只有在以 ISecret 类角色实现时,才可以调用此方法。
3、依赖反转
interface IPhone {void Dial();void PickUp();void Send();void Receive();}class PhoneUser {private IPhone _phone;public PhoneUser(IPhone phone) { _phone = phone; }public void UsePhone() { _phone.Dial(); _phone.PickUp(); _phone.Send(); _phone.Receive(); }}class XiaoMiPhone: IPhone {public void Dial() { Console.WriteLine("XiaoMi Dial working."); }public void PickUp() { Console.WriteLine("XiaoMi PickUp working."); }public void Send() { Console.WriteLine("XiaoMi Send working."); }public void Receive() { Console.WriteLine("XiaoMi Receive working."); }}static void Main() {// 用户与手机就实现了解耦。接口是用户和手机的“契约”// 如果有其他手机类,只需要实例化不同的手机即可,phone 并不需要更改代码 var user = new PhoneUser(new XiaoMiPhone()); user.UsePhone();}4、接口隔离
尽量避免“胖接口”带来的冗余与不兼容性。
class Driver {// driver 只需要实现驾驶的功能,因此只需要实现 IVehicle 内的功能private IVehicle _vehicle;public Driver(IVehicle vehicle) { _vehicle = vehicle; }public void Drive() { _vehicle.Run(); }}interface IVehicle {void Run();}interface IWeapon {void Fire();}class Car: IVehicle {public void Run() { Console.WriteLine("Car running."); }}class Tank: IVehicle, IWeapon {public void Run() { Console.WriteLine("Tank running."); }public void Fire() { Console.WriteLine("Tank fired!"); }} 如果 Fire()、Run() 整合到一个接口中,会导致接口粒度过大,无法对使用方提供很好的兼容效果。
5、反射与依赖注入
反射:以不变应万变。
反射的实现:
using System.Reflection;class Program {static void Main() { ITank tank = new Tank(); var t = tank.GetType(); object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t); MethodInfo fireMi = t.GetMethod("Fire"); MethodInfo runMi = t.GetMethod("Run"); fireMi.Invoke(o, null); fireMi.Invoke(o, null); }} 依赖反转:如果在类 A 的内部去实例化类 B,那么两者之间会出现较高的耦合。要解决这个问题,就要把 A类对 B 类的控制权抽离出来,交给一个第三方去做,把控制权反转给第三方(一般称 IOC 容器,即实现 IOC 的组件或框架),就称作控制反转(IOC Inversion Of Control)。
依赖注入:是实现依赖反转的一种方法。
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;class Program {static void Main() { var sc = new ServiceCollection(); sc.AddScoped(typeof(ITank), typeof(MediumTank)); sc.AddScoped(typeof(IVehicle), typeof(Car)); sc.AddScoped<Driver>(); var sp = sc.BuildServiceProvider();// 实例化 tank 时,借助 IOC 容器 var tank = sp.GetService<Itank>(); tank.Fire(); tank.Run();// 实例化 driver 时,由于 Driver 内有实现 IVehicle 的成员,// 而 IVehicle 已经注册实例化 Car,因此 driver 内将组合 Car 类对象 var driver = sp.GetService<Driver>(); driver.Drive(); }}Q.E.D.